概述
ThreadLocal 是 java 提供的一个方便对象在本线程内不同方法中传递和获取的类。用它定义的变量,仅在本线程中可见和维护,不受其他线程的影响,与其他线程相互隔离。
虽然在本线程不同方法中使用变量,可以通过在方法中传入参数解决,但是当涉及多个方法甚至多个类时,为每个方法增加同样的参数将是一场噩梦,此时 ThreadLocal 就能很好地解决这个问题。它可以在本线程内任何一个地方赋值,在任何一个地方获取值,并且不用作为函数参数传入。这看起来像静态成员变量,但是 ThreadLocal 变量相比静态成员变量的一个优势就是,ThreadLocal 是线程隔离的,其值不会受另一个线程的影响,也不用考虑加锁或值被其他线程篡改的问题,而这些问题都是静态成员变量无法做到的。因此当涉及一个对象需要在很多不同方法之间传递时,应该考虑使用 ThreadLocal 对象来简化代码。
使用
ThreadLocal 通过 set 方法可以给变量赋值,通过 get 方法获取变量的值。当然,也可以在定义变量时通过 ThreadLocal.withInitial 方法给变量赋初始值,或者定义一个继承 ThreadLocal 的类,然后重写 initialValue 方法。
示例代码如下
1 | public class TestThreadLocal |
在例子中,定义了一个 builder 的 ThreadLocal 对象,然后启动 5 个线程,分别对 builder 对象进行访问和修改操作,这两个操作放在两个不同的函数 append、change 中进行,两个函数访问 builder 对象也是直接获取,而不是放入函数的入参中传递进来。
代码输出如下
1 | thread-0 append 0, now builder value is 0, ThreadLocal instance hashcode is 796465865, ThreadLocal instance mapping value hashcode is 566157654 |
从输出中 1~6 行可以看出,不同线程访问的是同一个 builder 对象(不同线程输出的 ThreadLocal instance hashcode 值相同),但是每个线程获得的 builder 对象存储的实例 StringBuilder 不同(不同线程输出的 ThreadLocal instance mapping value hashcode 值不相同)。
从输出中 1~2、9~10行可以看出,同一个线程中修改 builder 对象存储的实例的值时,并不会影响到其他线程的 builder 对象存储的实例(thread-4 线程改变存储的 StringBuilder 的值并不会引起 thread-0 线程的 ThreadLocal instance mapping value hashcode 值发生改变)
从输出中 9~13 行可以看出,一个线程对 ThreadLocal 对象存储的值发生改变时,并不会影响其他的线程(thread-0 线程调用 set 方法改变本线程 ThreadLocal 存储的对象值,本线程的 ThreadLocal instance mapping value hashcode 发生改变,但是 thread-4 的 ThreadLocal instance mapping value hashcode 并没有因此改变)。
原理
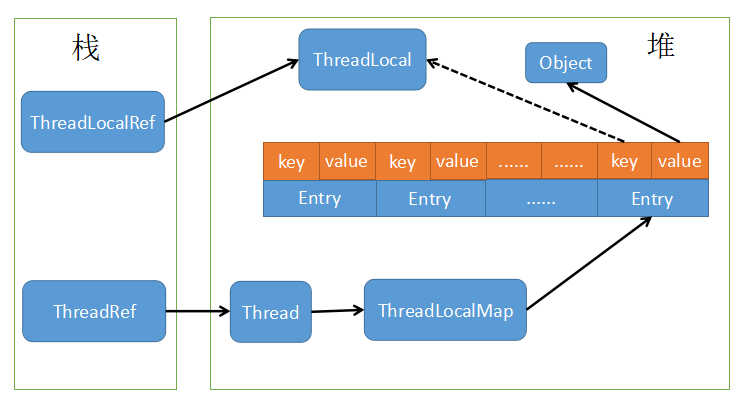
ThreadLocal 能在每个线程间进行隔离,其主要是靠在每个 Thread 对象中维护一个 ThreadLocalMap 来实现的。因为是线程中的对象,所以对其他线程不可见,从而达到隔离的目的。那为什么是一个 Map 结构呢。主要是因为一个线程中可能有多个 ThreadLocal 对象,这就需要一个集合来进行存储区分,而用 Map 可以更快地查找到相关的对象。
ThreadLocalMap 是 ThreadLocal 对象的一个静态内部类,内部维护一个 Entry 数组,实现类似 Map 的 get 和 put 等操作,为简单起见,可以将其看做是一个 Map,其中 key 是 ThreadLocal 实例,value 是 ThreadLocal 实例对象存储的值。
set
当调用 ThreadLocal 的 set 方法给变量设置值时,ThreadLocal 对象会先获取本线程的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,然后将当前的 ThreadLocal 对象及要设置值作为键值对放入 Map 中。
1 | public void set(T value) { |
get
获取 ThreadLocal 存储的对象值时,需要调用 get 方法。此方法也是先获取本线程的 ThreadLocalMap 对象,然后将当前的 ThreadLocal 对象作为 key 从 Map 中获取对应的值,如果没有,则返回一个初始 null。
1 | public T get() { |
内存泄漏
ThreadLocalMap 中的 key 是一个 ThreadLocal 对象,且是一个弱引用,而 value 却是一个强引用。
1 | static class ThreadLocalMap { |
毫无疑问,如果线程执行完关闭,那么线程的所有对象都会被销毁,此时不会存在内存泄漏的问题。此外,在执行 get、set 操作时,调用进入 ThreadLocalMap 内部的函数,会对 Entry 进行检查,如果 key 为空,也会将 value 设置为空,让其可以被垃圾回收。所以一般情况下也不会造成内存泄漏。
1 | // get 或 set 方法,满足一定条件时会进入 expungeStaleEntry 方法 |
但是,存在一种情况,可能导致内存泄漏。如果在某一时刻,将 ThreadLocal 实例设置为 null,即没有 ThreadLocal 没有强引用了,如果发生 GC 时,由于 ThreadLocal 实例只存在弱引用,所以被回收了,但是 value 仍然存在一个当前线程连接过来的强引用,其不会被回收,只有等到线程结束死亡或者手动清空 value 或者等到另一个 ThreadLocal 对象进行 get 或 set 操作时刚好触发 expungeStaleEntry 函数并且刚好能够检查到本 ThreadLocal 对象 key 为空(概率太小),这样才不会发生内存泄漏。否则,value 始终有引用指向它,它也不会被 GC 回收,那么就会导致内存泄漏。虽然发生内存泄漏的概率比较小,但是为了保险起见,也建议在使用完 ThreadLocal 对象后调用一下 remove 方法清理一下值。
与线程池结合使用
由于线程池是会复用线程的,因此如果在线程任务中对 ThreadLocal 没有经过重新设值而直接读取值的话,可能读取到的是该线程上一个任务赋值的结果,而不是本次任务的初始值,从而导致一些意向不到的错误。如下所示,创建一个固定大小是 3 的线程池,但是往线程池中放入 5 个任务,则最后两个任务会复用之前创建的线程,此时调用 ThreadLocal 的 get 方法获取到的是上一个任务赋值的结果,而不是本线程的初始值(程序输出的第4~5 行就是复用了线程 11 和 13,第一次获取到的是也是上一个任务赋的值 2,而不是本线程的初始值 1)。
1 | public class TestThreadLocalExecutor |
程序输出如下
1 | Thread id: 11, before increment: 1, after increment: 2 |
为了避免如上情况的发生,可以在每个任务开始时,为 ThreadLocal 对象重新设置初始值(在 get 方法前先调用 set 方法),或者使用原生的创建线程的方式(跳开线程池的方式)。